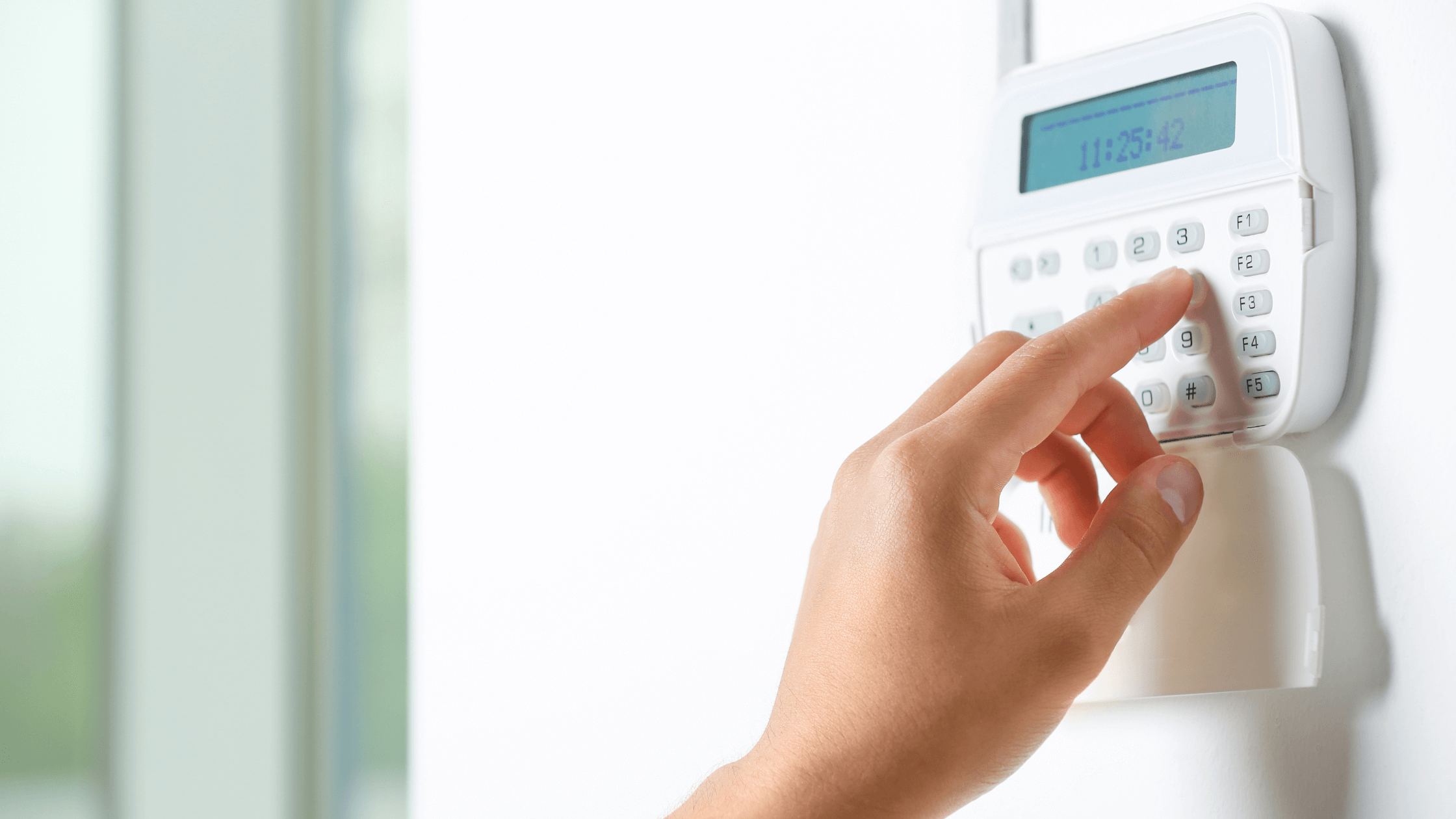
In today’s world, where safety and security are paramount, the role of alarm systems within Electrical Infrastructure, much like the various types of electrical panels, cannot be overstated. Alarm systems serve as the frontline defense against unauthorized intrusions, fires, and other emergencies. This blog post delves into the different types of alarm systems available, each tailored to meet specific security needs. From traditional wired setups to advanced wireless configurations, the diversity and sophistication of these systems, much like the evolution of types of electrical boxes and types of electrical outlets, have advanced significantly.
Understanding the different types of alarm systems is crucial for homeowners, business owners, and security professionals alike. Similar to selecting the right types of fuses or types of electrical outlets, choosing the appropriate alarm system ensures that security needs are effectively met. As we explore these types, we’ll uncover the intricacies and benefits of each, providing valuable insights into the world of modern security solutions.
What is an Alarm System?
An alarm system, in its essence, is a setup designed to alert property owners or security services about potential threats such as intrusions, fires, or environmental dangers. These systems play a crucial role in safeguarding homes, businesses, and public spaces.
The history of alarm systems dates back several decades, evolving from simple mechanical contraptions to sophisticated, technology-driven solutions. Originally, these systems were primarily focused on detecting unauthorized entry, but over time, their functionality has expanded to include a variety of sensors for smoke, carbon monoxide, water leaks, and more.
At the core of every alarm system, regardless of its type, is the principle of detection and notification. Detection involves sensing an anomaly, such as a break-in or a fire, using various types of sensors. Once detected, the system triggers a response – typically, an audible alarm and, in many cases, an automatic notification to the property owner or a monitoring center.
Today, we have diverse types of alarm systems, each offering unique features and technologies suited to different environments and security needs. Whether it’s a wired system connected through physical cables or a wireless system utilizing radio frequencies, each type ensures that individuals and assets are kept safe from a variety of risks. As we proceed to explore the different types of alarm systems, it’s important to understand the fundamental purpose they serve: providing peace of mind and safety to those who rely on them.
Different Types of Alarm Systems
The 4 main types of alarm system are:
- Wired Alarm Systems
- Wireless Alarm Systems
- Unmonitored Alarm Systems
- Monitored Alarm Systems
Types of Alarm Systems 1: Wired Alarm Systems
Working Principles of Wired Alarm Systems
Wired alarm systems function by connecting various sensors and detectors to a central control panel through physical wires. When a sensor, such as a door or window contact, detects an intrusion or any other irregular activity, it sends a signal via these wires to the control panel. The control panel then activates the alarm, which could be a loud siren, flashing lights, or both. Some wired systems are also connected to a monitoring service, which is alerted simultaneously.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Wired Alarm Systems
Advantages:
- Reliability: Wired alarm systems are less prone to interference and signal loss, ensuring consistent performance.
- No Batteries Required: Sensors in a wired system are powered by the main system, eliminating the need for regular battery replacements.
- Tamper-Resistant: The physical connections make it more challenging for intruders to disable the system without detection.
Disadvantages:
- Installation Complexity: Installing a wired system often requires professional assistance and can be intrusive, especially in finished homes.
- Less Flexibility: Moving or expanding a wired system can be difficult and costly due to the physical wiring involved.
- Vulnerability to Power Outages: Unless backed up by a battery, wired systems can be incapacitated during power outages.
Characteristics of Wired Alarm Systems
Wired alarm systems typically feature a variety of components such as motion detectors, door/window contacts, glass break sensors, and environmental detectors. They are known for their robustness and are often used in larger properties where installation can be planned during the construction phase. These types of alarm systems are also favorable in settings where wireless signals might be weak or unreliable.
Use Cases for Wired Alarm Systems
These types of alarm systems are ideal for permanent installations in residential homes, commercial buildings, and industrial settings. They are particularly suited for large structures where long-term reliability is a priority. These systems are also preferred in environments where wireless signals may face interference, such as buildings with thick walls or heavy electronic equipment.
Types of Alarm Systems 2: Wireless Alarm Systems
Working Principles of Wireless Alarm Systems
Wireless alarm systems operate on the principle of radio frequency signals. Sensors placed around the property communicate wirelessly with a central control panel. When a sensor (like a motion detector or door sensor) is triggered, it sends a radio signal to the control panel, which then activates the alarm. This activation may include sounding a siren, sending an alert to the homeowner’s mobile device, or notifying a monitoring service, depending on the system’s configuration.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Wireless Alarm Systems
Advantages:
- Ease of Installation: Wireless systems can be installed quickly and without the need for drilling or complex wiring, making them ideal for existing homes and buildings.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Adding or relocating sensors is straightforward, allowing for easy expansion as security needs change.
- Remote Monitoring: Many wireless systems offer smart capabilities, enabling homeowners to monitor and control their system remotely via smartphones or tablets.
Disadvantages:
- Battery Dependency: Wireless sensors require batteries, which need regular checking and replacement.
- Range Limitations: The effective range of wireless signals can be limited, especially in larger properties or buildings with thick walls.
- Potential for Interference: Wireless systems can sometimes face interference from other wireless devices, which may affect performance.
Characteristics of Wireless Alarm Systems
Wireless alarm systems are known for their portability and ease of use. They often come with user-friendly interfaces and can integrate seamlessly with other smart home devices. These systems are especially popular in residential settings due to their non-intrusive installation and the ability to be customized to various home layouts.
Use Cases for Wireless Alarm Systems
These types of alarm systems are a go-to choice for residential properties, small businesses, and rental properties where installation flexibility is key. They are also well-suited for historic buildings or locations where preserving the integrity of the structure is important. Additionally, for those seeking to integrate their alarm system with other smart home technologies, wireless systems offer the necessary compatibility and ease of integration.
Types of Alarm Systems 3: Unmonitored Alarm Systems
Working Principles of Unmonitored Alarm Systems
Unmonitored alarm systems, also known as self-monitored systems, function independently without the need for a professional monitoring service. These systems typically consist of a series of sensors connected to a central alarm unit. When a sensor is triggered — for instance, by a door opening or motion being detected — the system responds by activating an audible alarm or lights. Additionally, These types of alarm systems can send alerts directly to the homeowner’s smartphone or tablet, allowing them to assess the situation and take appropriate action, such as contacting the authorities.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Unmonitored Alarm Systems
Advantages:
- No Monthly Fees: Since these systems don’t require professional monitoring, there are no ongoing fees associated with their use.
- Direct Control: Homeowners have direct control over their security system and response protocols.
- Easy Installation: Many unmonitored systems are wireless, making them easy to install and configure.
Disadvantages:
- Responsibility for Monitoring: The homeowner is solely responsible for responding to alarms, which can be a challenge if they are away or unable to check their phone.
- Limited Response: Without a monitoring service, there’s no automatic notification to emergency services, which could delay response times in a real emergency.
- Potential for False Alarms: Without professional verification, there’s an increased risk of false alarms leading to unnecessary stress or nuisance.
Characteristics of Unmonitored Alarm Systems
Unmonitored alarm systems are typically more straightforward in design compared to monitored systems. They often include a combination of door and window sensors, motion detectors, and a central alarm unit. Many also integrate with home automation systems and offer remote access and control through mobile apps.
Use Cases for Unmonitored Alarm Systems
These types of alarm systems are well-suited for homeowners and renters who prefer a hands-on approach to their home security and are comfortable with the responsibility of self-monitoring. They are also a popular choice for small businesses and properties where the owner is frequently on-site. These systems are ideal for those looking for a cost-effective, no-frills security solution that provides basic protection without the need for professional monitoring services.
Types of Alarm Systems 4: Monitored Alarm Systems
Working Principles of Monitored Alarm Systems
Monitored alarm systems are designed to provide an extra layer of security by connecting the alarm system to a professional monitoring service. These systems consist of various sensors and a control panel. When a sensor is activated, such as by a break-in or smoke detection, the signal is not only used to trigger an onsite alarm but also sent to a monitoring center. Operators at the center then assess the situation and can notify the property owner and appropriate emergency services if necessary.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Monitored Alarm Systems
Advantages:
- Professional Response: The involvement of a monitoring service ensures that every alarm is evaluated and responded to promptly, even if the property owner is unavailable.
- Enhanced Security: These systems often deter potential intruders more effectively, knowing that a professional response is imminent.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Monitored systems can include a range of protection, from burglary to environmental hazards like fire and gas leaks.
Disadvantages:
- Monthly Fees: The ongoing cost of monitoring services can be a significant factor for some property owners.
- Contract Commitments: Many monitored systems require long-term contracts with the monitoring service provider.
- Dependency on External Services: The system’s effectiveness relies on the monitoring center’s response, which can be influenced by external factors like network issues or center workload.
Characteristics of Monitored Alarm Systems
Monitored alarm systems are comprehensive, often integrating various types of sensors, including intrusion, fire, flood, and carbon monoxide detectors. These types of alarm systems typically offer high-end features like remote access, home automation compatibility, and sometimes even video surveillance. These systems are designed to provide a comprehensive security solution that goes beyond basic deterrence.
Use Cases for Monitored Alarm Systems
These types of alarm systems are ideal for residential properties, especially those in high-risk areas or left unattended for long periods. They are also extensively used in commercial and industrial settings where constant surveillance and immediate response to incidents are critical. These systems are particularly beneficial for individuals who prefer the peace of mind that comes with knowing professionals are overseeing their property’s security around the clock.
Comparative Analysis
In this section, we provide a comparative analysis of the four types of alarm systems discussed: Wired, Wireless, Unmonitored, and Monitored. This comparison will help in understanding the distinct features, benefits, and potential limitations of each system, aiding in making an informed decision based on individual needs and circumstances.
| Feature | Wired Alarm Systems | Wireless Alarm Systems | Unmonitored Alarm Systems | Monitored Alarm Systems |
| Installation | Complex, often requires professional installation | Easy and DIY-friendly | Generally easy and DIY-friendly | Varies, but often requires professional installation |
| Cost | Higher upfront due to installation | Moderate upfront, lower overall | Lower overall, no monthly fees | Monthly fees, higher overall cost |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, less interference | Subject to signal interference | Dependent on homeowner’s monitoring | Highly reliable with professional monitoring |
| Flexibility | Limited, difficult to modify or expand | Highly flexible and easy to expand | Flexible, easy to adjust settings | Varies, but generally less flexible |
| Power Supply | Mainly hardwired, may have battery backup | Battery-powered sensors | Battery-powered or main power | Typically main power with battery backup |
| Range | Not limited by signal range | Limited by signal range, extenders available | Varies, generally not an issue | Depends on system specifications |
| Remote Access | Limited, depends on the system | Commonly available | Commonly available, dependent on system | Commonly available |
| Response Type | Sirens, and lights, can connect to the monitoring | Sirens, alerts to phone/app | Sirens, alerts to phone/app | Professional monitoring service response |
| Best Use Cases | Large properties, new constructions | Residential homes, renters | Homeowners comfortable with self-monitoring | Properties needing 24/7 surveillance and response |
Any one of these types of alarm systems offers unique advantages and challenges. Wired systems are known for their reliability and are ideal for large properties or new constructions where installation can be integrated into the building process. Wireless systems offer flexibility and ease of installation, making them a popular choice for residential homes and renters. Unmonitored systems cater to those who prefer to handle their security independently, without the need for ongoing fees. Monitored systems provide the highest level of security with professional oversight, suitable for properties requiring round-the-clock surveillance and rapid emergency response.
The choice of an alarm system depends on factors such as property size, lifestyle, security needs, and budget considerations. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right alarm system for effective and efficient security management.
Conclusion
The exploration of the different types of alarm systems reveals a diverse range of options available to suit varying security needs. From wired systems known for their reliability to wireless systems that offer unparalleled flexibility, and from self-monitored systems that empower homeowners to professionally monitored systems that provide peace of mind through continuous surveillance, the choice depends on individual requirements and preferences. Understanding the workings, advantages, and limitations of different types of alarm systems is crucial in making an informed decision.
The right alarm system not only protects property and lives but also offers a sense of security and comfort. Whether for a home, business, or special property, the investment in an appropriate alarm system is an investment in safety and peace of mind.
FAQs
- What are the different types of alarm systems?
The main types of alarm systems are Wired, Wireless, Unmonitored, and Monitored. Each type offers unique features: Wired systems are reliable and suited for large properties, Wireless systems provide flexibility and ease of installation, Unmonitored systems allow for self-monitoring without monthly fees, and Monitored systems offer the highest level of security with professional monitoring services. - How do I choose the right types of alarm systems for my needs?
Choosing the right alarm system depends on several factors: the size and layout of your property, your lifestyle, the level of security you need, and your budget. Consider whether you need professional monitoring, the ease of installation, and the flexibility to expand the system in the future. - What are the main differences between wired and wireless types of alarm systems?
The main difference between these two types of alarm systems lies in their installation and flexibility. Wired systems require physical connections and are more complex to install but are highly reliable. Wireless systems use radio frequency signals, are easier to install and expand, but can be subject to signal interference. - Are unmonitored alarm systems effective?
These types of alarm systems can be effective, especially in alerting homeowners about potential security breaches. However, their effectiveness depends on the homeowner’s ability to respond to alerts. They do not provide automatic notification to emergency services, which is a key feature of monitored systems.