Welcome to our comprehensive guide on “Types of Modules in Electronics”! In the ever-evolving world of electronics, modules play a vital role in simplifying complex functionalities and enabling seamless integration within Data and Control Systems. These compact and versatile units have revolutionized how electronic systems are designed, developed, and utilized across various industries.
In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating realm of electronic modules, uncovering the diverse array of modules available and exploring their unique functions and applications. We’ll also explore how Types of Microprocessors, Types of Flip Flops, Types of Comparators, and Types of Memory Modules contribute to the functionality and efficiency of modern electronic devices.
From communication modules that facilitate data transfer and sensor modules that capture the world around us to power modules ensuring efficient energy management, each type of module contributes uniquely to advancing electronic technology. Whether you’re a hobbyist working on DIY projects, an engineer innovating cutting-edge solutions, or someone curious about electronics, join us on this journey as we explore the world of “Types of Modules in Electronics.” Let’s get started!
Basics of Modules
Electronic modules are essentially building blocks of electronic systems, carefully engineered to consolidate specific functionalities, components, or circuits within a compact and self-contained package. These modules serve as stand-alone entities, each with a unique purpose and set of capabilities, making them highly versatile and adaptable to a wide range of applications.
One of the primary advantages of electronic modules is their plug-and-play nature. By encapsulating the necessary components and functionalities within a single unit, they can seamlessly integrate into larger electronic systems without requiring extensive redesign or complex wiring. This modular approach significantly streamlines the overall design process, reducing development time and costs.
Moreover, the use of electronic modules enhances the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Since each module is designed and tested independently, they undergo rigorous quality control and validation procedures, ensuring consistent and dependable performance. This isolation also simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance, as faulty modules can be easily replaced without affecting the entire system.
The modularity of electronic modules also promotes scalability and upgradability. Engineers and designers can mix and match modules to tailor electronic systems for specific needs, allowing for flexibility in customization and future enhancements. This scalability is particularly advantageous in rapidly evolving industries, where new functionalities and features are constantly being developed.
Additionally, electronic modules contribute to reducing complexities in manufacturing processes. By outsourcing the production of specific modules to specialized manufacturers, companies can focus on the integration and assembly of these modules into their end products. This division of labor optimizes production efficiency and lowers production costs, which can ultimately lead to more affordable and accessible electronic devices for consumers.
Overall, electronic modules have revolutionized the electronics industry by providing a modular and flexible approach to designing electronic systems. With their self-contained nature, seamless integration capabilities, and enhanced performance, these modules have become an indispensable part of modern electronic devices, driving innovation and improving the functionality of various technologies across numerous sectors. As technology continues to advance, electronic modules are expected to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of electronics.
Different Types of Modules in Electronics
Here is a list of different types of modules in electronics:
1. Communication Modules:
- Bluetooth Modules
- Wi-Fi Modules
- Zigbee Modules
- Cellular Modules (e.g., GSM, LTE)
- LoRa Modules
2. Sensor Modules:
- Temperature Sensor Modules
- Humidity Sensor Modules
- Proximity Sensor Modules
- Motion Sensor Modules (e.g., Accelerometer, Gyroscope)
- Light Sensor Modules
- Gas Sensor Modules
3. Power Modules:
- Voltage Regulator Modules
- DC-DC Converter Modules
- Power Amplifier Modules
- Battery Management Modules
4. Display Modules:
- LCD Display Modules
- OLED Display Modules
- LED Matrix Modules
5. Interface Modules:
- USB Modules
- I2C Modules
- SPI Modules
- UART Modules
- Ethernet Modules
6. Memory Modules:
- RAM Modules
- Flash Memory Modules
- EEPROM Modules
7. Audio Modules:
- Audio Amplifier Modules
- Audio Codec Modules
- Speaker Modules
8. Motor Control Modules:
- DC Motor Control Modules
- Stepper Motor Control Modules
- Servo Motor Control Modules
9. Application-Specific Modules:
- GPS Modules
- Camera Modules
- Biometric Modules (e.g., Fingerprint, Iris scanners)
- RFID Modules
10. RF (Radio Frequency) Modules:
- RF Transmitter Modules
- RF Receiver Modules
- RF Transceiver Modules
11. Power Supply Modules:
- AC-DC Power Supply Modules
- DC-AC Power Inverter Modules
12. Wireless Charging Modules:
- Wireless Charging Receiver Modules
- Wireless Charging Transmitter Modules
13. IoT (Internet of Things) Modules:
- IoT Communication Modules (e.g., MQTT, CoAP)
- IoT Node Modules (e.g., ESP8266, ESP32)
14. Embedded System Modules:
- Microcontroller Modules (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) Modules
15. RFID/NFC (Near Field Communication) Modules:
- RFID Reader Modules
- NFC Tag Modules
These are just a few examples of the diverse types of modules available in the electronics industry. Each type of module serves a specific purpose, and their integration enables the development of complex electronic systems for various applications.
Communication Modules
Communication modules are an integral part of modern electronics, facilitating the exchange of data between devices and systems over various communication protocols. These compact and versatile units have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, enabling wireless connectivity and transforming the world into a connected global village. In this section, we will explore the different types of communication modules and their essential role in modern electronic devices.
Bluetooth Modules
Bluetooth modules are ubiquitous in today’s tech-savvy world, enabling short-range wireless communication between devices. They operate on the Bluetooth protocol and facilitate data transfer for applications like wireless audio streaming (e.g., Bluetooth speakers and headphones), file sharing between smartphones and tablets, and even IoT devices connecting to smartphones for remote control.
Wi-Fi Modules
Wi-Fi modules empower devices to connect to the internet and local area networks (LANs) wirelessly. These modules follow the Wi-Fi standard (IEEE 802.11), and they are found in smartphones, laptops, smart home devices, and a plethora of IoT gadgets. Wi-Fi modules enable seamless internet access, web browsing, cloud connectivity, and smart home automation.
Zigbee Modules
Zigbee modules cater to low-power, low-data-rate applications that require reliable communication between devices over short distances. They find applications in home automation, industrial monitoring, and smart lighting systems. Zigbee’s mesh network architecture allows for scalable and robust communication between a large number of devices.
Cellular Modules
Cellular modules, commonly known as GSM (2G), LTE (4G), or 5G modules, provide internet connectivity to devices over cellular networks. These modules are commonly found in smartphones, tablets, GPS trackers, and M2M (machine-to-machine) devices, enabling constant connectivity and data transfer over long distances.
LoRa Modules
LoRa (long-range) modules are designed for long-range communication with low power consumption, making them ideal for IoT applications where battery life is critical. LoRa modules operate on the LoRaWAN protocol, enabling devices to communicate over several kilometers without the need for complex infrastructure.
NFC Modules
Near Field Communication (NFC) modules enable contactless data exchange between devices by bringing them nearby. NFC technology is commonly used for mobile payments (e.g., contactless payments with smartphones), access control, and simplified pairing of Bluetooth devices.
Ethernet Modules
Ethernet modules facilitate wired communication between devices over local area networks (LANs). They are commonly used in computers, routers, switches, and other networked devices to achieve high-speed and reliable data transfer.
Satellite Communication Modules
Satellite communication modules enable data exchange over long distances, even in remote areas without terrestrial network coverage. They find applications in satellite phones, asset tracking, and communication in areas with limited infrastructure.
Communication modules have played a pivotal role in shaping the way we connect and interact with electronic devices and the world around us. Their versatility and reliability have made them indispensable in various industries, from consumer electronics to industrial automation and the Internet of Things (IoT). As technology continues to advance, these modules will continue to evolve, driving further innovations and creating a more interconnected and communicative future.

Sensor Modules
Sensor modules are the eyes and ears of electronic devices, allowing them to perceive and interact with the surrounding environment. These intelligent units house a wide range of sensors, each designed to detect specific physical phenomena. By converting real-world data into electrical signals, sensor modules play a pivotal role in enabling automation, data analysis, and decision-making in modern electronics. In this section, we will explore the fascinating world of sensor modules and the diverse applications they serve.
Temperature Sensor Modules
Temperature sensor modules are among the most common types of sensor modules. They measure the ambient temperature and provide valuable data for climate control, industrial processes, weather monitoring, and even wearable health devices.
Humidity Sensor Modules
Humidity sensor modules are designed to measure the moisture content in the air. These modules are crucial for applications such as weather stations, HVAC systems, agriculture, and storage facilities, where humidity levels can impact product quality and preservation.
Proximity Sensor Modules
Proximity sensor modules detect the presence or absence of an object within a specific range without physical contact. They are often used for touchless control, object detection, and gesture recognition in devices like smartphones, automatic doors, and industrial automation systems.
Motion Sensor Modules
Motion sensor modules detect movement and orientation changes. They include accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. These modules are essential components in smartphones, gaming controllers, fitness trackers, and navigation systems.
Light Sensor Modules
Light sensor modules measure the intensity of light in their surroundings. They find applications in automatic lighting systems, smartphone brightness adjustment, photography, and ambient light detection for displays.
Gas Sensor Modules
Gas sensor modules detect the presence and concentration of specific gases in the air. They are critical for safety applications, indoor air quality monitoring, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring.
Pressure Sensor Modules
Pressure sensor modules measure atmospheric pressure or fluid pressure. They are used in weather forecasting, altimeters, barometers, and various industrial and automotive applications.
Image Sensor Modules
Image sensor modules capture visual data and convert it into electronic signals. They are the core component in cameras and imaging systems, including those found in smartphones, digital cameras, and surveillance devices.
Biometric Sensor Modules
Biometric sensor modules are used for identifying and authenticating individuals based on unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial features. They are commonly found in smartphones, access control systems, and security devices.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) Modules
IMU modules combine multiple motion sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, to provide comprehensive motion-tracking data. They are used in robotics, virtual reality systems, and motion-capture applications.
Sensor modules are at the heart of the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution, providing the data needed for intelligent decision-making and automation. From smart home devices to industrial monitoring systems, sensor modules play a vital role in making our lives more efficient, convenient, and safer. As technology continues to advance, sensor modules will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, opening up new opportunities and applications in the world of electronics.
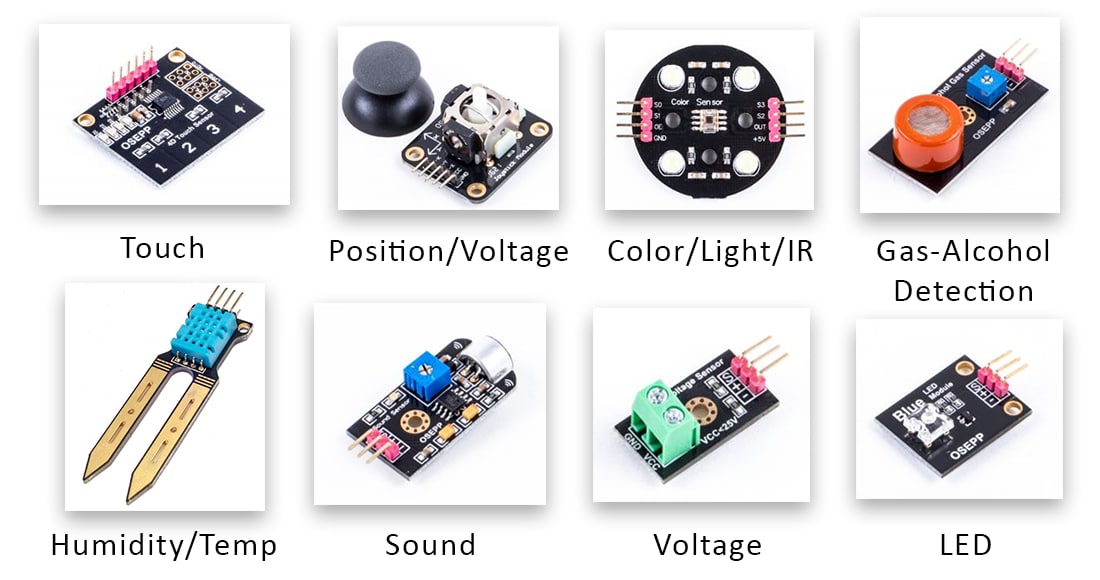
Power Modules
Power modules are essential components in electronic systems, responsible for managing and regulating the flow of electrical energy. These specialized units play a critical role in ensuring that electronic devices and circuits receive a stable and reliable power supply. By efficiently converting and distributing power, power modules enhance the performance, longevity, and safety of various electronic applications. In this section, we will explore the world of power modules and their significance in modern electronics.
Voltage Regulator Modules
Voltage regulator modules (VRMs) are crucial for maintaining a steady and constant output voltage despite fluctuations in the input voltage or load conditions. These modules are commonly used in power supplies for microcontrollers, digital circuits, and electronic components that require precise and stable voltage levels.
DC-DC Converter Modules
DC-DC converter modules convert electrical energy from one DC voltage level to another. They are extensively used in various electronic devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and battery-powered systems, to efficiently step up or step down the voltage as needed.
Power Amplifier Modules
Power amplifier modules are designed to amplify electrical signals, primarily for audio or radio frequency (RF) applications. They are found in audio systems, wireless communication devices, and RF transmitters, providing the necessary signal boost for improved performance.
Battery Management Modules
Battery management modules (BMS) are crucial for the safe and efficient operation of rechargeable batteries. They monitor battery parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature, ensuring optimal charging, discharging, and protection against overcharging or overheating.
Power Factor Correction (PFC) Modules
Power factor correction modules improve the power factor of electrical systems by minimizing reactive power and enhancing overall energy efficiency. PFC modules are commonly used in high-power applications, such as industrial equipment and power distribution systems.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Modules
UPS modules provide backup power to critical electronic devices in case of a main power failure. They are commonly used in computers, servers, and data centers, ensuring continuous operation and protecting against data loss or damage.
Motor Driver Modules
Motor driver modules control and regulate the power supplied to electric motors. They are essential components in robotics, drones, automotive systems, and industrial automation, providing precise control over motor speed and direction.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Modules
PoE modules enable the transmission of both data and power over a single Ethernet cable. They find applications in IP cameras, access points, and IoT devices, simplifying installation and reducing the need for separate power sources.
Power Distribution Modules
Power distribution modules facilitate the efficient distribution of electrical power within a system or circuit. They are commonly used in complex electronic systems, ensuring that each component receives the appropriate power level without overloading any part of the system.
Current Limiting Modules
Current limiting modules protect electronic components from excessive current flow, preventing damage or failure due to overload conditions. They are used in power supplies, battery charging circuits, and electronic devices where current regulation is essential.
Power modules are the backbone of electronic systems, providing the necessary energy management and regulation for smooth and reliable operation. From maintaining stable voltages to efficiently distributing power, these modules are vital in enabling the functionality and longevity of electronic devices across various industries and applications. As technology advances, power modules will continue to evolve, becoming more efficient, compact, and integral to the next generation of electronic innovations.

Display Modules
Display modules are essential components in electronic devices, serving as the interface between users and the digital world. These intelligent units enable the presentation of information, graphics, and multimedia in a visually appealing and user-friendly manner. From small screens on handheld devices to large displays in public spaces, display modules have transformed the way we interact with technology. In this section, we will explore the world of display modules and their diverse applications in modern electronics.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Modules
LCD modules are widely used for displaying text, images, and graphics in a variety of electronic devices. They operate on the principle of manipulating liquid crystals to control light transmission, providing a sharp and vibrant display. LCD modules are commonly found in smartphones, televisions, computer monitors, digital cameras, and various industrial applications.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) Modules
OLED modules are known for their superior color reproduction, contrast ratio, and thin form factor. Each pixel in an OLED display emits its light, eliminating the need for a backlight, resulting in deeper blacks and lower power consumption. OLED modules are used in high-end smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and TVs.
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) Matrix Modules
LED matrix modules consist of an array of individual LED elements arranged in rows and columns. They are versatile displays capable of showing text, graphics, animations, and even simple videos. LED matrix modules are commonly used in digital billboards, information displays, and large-scale signage.
E-Paper (Electronic Paper) Modules
E-paper modules mimic the appearance of traditional paper and consume very little power. They are commonly used in e-book readers, electronic shelf labels, and signage that requires static images and text. E-paper displays offer excellent readability in bright sunlight.
Touchscreen Modules
Touchscreen modules combine a display with touch-sensitive capabilities, allowing users to interact directly with the screen. Capacitive and resistive touchscreens are the most common types used in smartphones, tablets, ATMs, and other interactive devices.
TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) Modules
TFT modules are a type of LCD that uses thin-film transistors to control individual pixels. TFT displays offer faster response times, better color reproduction, and higher resolutions, making them suitable for high-quality graphics and video playback.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) Modules
AMOLED modules are an advanced form of OLED displays that use a thin-film transistor backplane for pixel control. They provide vibrant colors, high contrast, and power-efficient displays. AMOLED panels are commonly used in premium smartphones, smartwatches, and VR headsets.
Graphic LCD Modules
Graphic LCD modules are specialized displays that can render images and graphics directly from memory. They are commonly used in embedded systems, industrial control panels, and graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for various applications.
Character LCD Modules
Character LCD modules are designed to display fixed characters and symbols. They are commonly used in digital watches, calculators, and small appliances, providing simple and cost-effective visual feedback.
Microdisplay Modules
Microdisplay modules are miniature displays used in applications such as head-mounted displays, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) glasses, and digital cameras. They offer high-resolution and compact form factors for immersive experiences.
Display modules have revolutionized human-computer interaction, enabling seamless communication and enhancing the user experience in a wide range of electronic devices. From personal gadgets to large-scale digital signage, these modules continue to evolve, offering sharper visuals, higher resolutions, and innovative ways to present information and entertain users. As technology advances, display modules will play an even more integral role in shaping the future of human-machine interfaces.
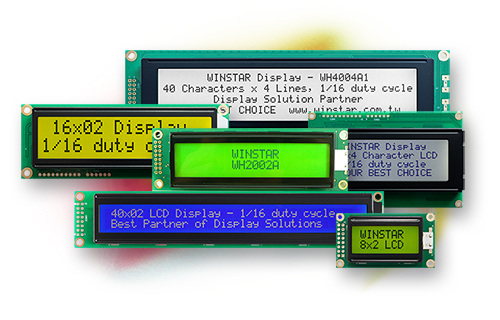
Interface Modules
Interface modules serve as crucial intermediaries, allowing different components and systems to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. These intelligent units facilitate the integration of diverse technologies, enabling electronic devices to work cohesively and efficiently. From simple communication protocols to complex data transfer mechanisms, interface modules play a vital role in the interconnected world of electronics. In this section, we will explore the diverse types of interface modules and their significance in modern electronic applications.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) Modules
USB modules provide a standardized and versatile interface for connecting peripheral devices to computers and other electronic devices. They enable data transfer, power delivery, and device charging, making them ubiquitous in various applications, such as external storage devices, keyboards, mice, and smartphones.
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) Modules
I2C modules are designed for serial communication between multiple components in a circuit. They enable simple and efficient data transfer between microcontrollers, sensors, memory chips, and other peripherals, making them ideal for various embedded systems.
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) Modules
SPI modules facilitate high-speed, full-duplex communication between a master and multiple slave devices. They are commonly used in applications that require fast data transfer, such as communication with external flash memory, sensors, and display controllers.
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) Modules
UART modules are essential for asynchronous serial communication between devices. They are commonly found in applications that require data transmission without a shared clock signal, such as GPS receivers, wireless modules, and Bluetooth communication.
Ethernet Modules
Ethernet modules enable wired communication between devices over local area networks (LANs). They are widely used in computer networks, routers, switches, and IoT devices to establish reliable and high-speed data connections.
CAN (Controller Area Network) Modules
CAN modules are designed for robust and fault-tolerant communication in automotive and industrial applications. They are commonly used in vehicles, industrial automation systems, and distributed control networks.
RS-232 (Recommended Standard 232) Modules
RS-232 modules are used for serial communication over long distances. Although it has become less common in recent years, RS-232 is still used in legacy systems, industrial applications, and communication with older peripherals.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) Modules
HDMI modules enable high-definition audio and video transmission between electronic devices. They are commonly used in televisions, monitors, projectors, and multimedia systems, providing high-quality digital audio and video signals.
CAN Bus Modules
CAN bus modules provide a standardized protocol for communication in automotive applications. They enable data exchange between electronic control units (ECUs) in vehicles, allowing for seamless integration of various automotive systems.
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) Modules
PCIe modules offer high-speed data transfer between components in computers and embedded systems. They are commonly used in graphics cards, storage devices, and other high-performance peripherals.
Interface modules play a pivotal role in enabling interoperability between electronic components and systems. Their standardized communication protocols and data transfer mechanisms have revolutionized the way devices interact and exchange information, paving the way for the seamless integration of technologies and the development of complex and interconnected electronic systems. As technology continues to advance, interface modules will remain at the forefront of driving innovation and shaping the future of electronics.

Memory Modules
Memory modules are essential components in electronic devices, responsible for storing and retrieving data for various applications. These intelligent units come in different forms and capacities, providing temporary or permanent data storage to meet the diverse needs of modern electronics. From temporary data storage in active applications to long-term data retention in non-volatile memory, memory modules play a pivotal role in enhancing the functionality and performance of electronic devices. In this section, we will explore the different types of memory modules and their significance in the world of electronics.
RAM (Random Access Memory) Modules
RAM modules are volatile memory units that provide fast and temporary data storage for running applications. They enable quick access to data, allowing processors to execute tasks efficiently. RAM is used in computers, smartphones, gaming consoles, and other devices that require real-time data processing.
ROM (Read-Only Memory) Modules
ROM modules are non-volatile memory units that store data permanently. The data stored in ROM cannot be modified, making it suitable for critical system instructions and firmware. Examples of ROM include BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) in computers and firmware in microcontrollers.
Flash Memory Modules
Flash memory modules are non-volatile memory units that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. They are commonly used in USB drives, memory cards, solid-state drives (SSDs), and smartphones for data storage and transfer.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) Modules
EEPROM modules are non-volatile memory units that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed on a byte-by-byte basis. They are used for storing small amounts of critical data that may require frequent updates, such as configuration settings in electronic devices.
Cache Memory Modules
Cache memory modules are a special type of fast memory used to temporarily store frequently accessed data from slower main memory. They improve the overall performance of processors by reducing data access latency, making them vital in modern computing systems.
NVRAM (Non-Volatile Random Access Memory) Modules
NVRAM modules combine the benefits of both volatile and non-volatile memory, offering the speed of RAM with the data retention capabilities of non-volatile memory. They find applications in data storage and backup systems that require fast access and data persistence.
Virtual Memory Modules
Virtual memory modules are an extension of the physical RAM that uses a portion of the hard disk as an overflow for RAM. This allows systems to run more applications than physically available RAM and provides a larger address space for programs.
Register Files
Register files are a small and fast type of memory integrated into microprocessors. They store data that the processor is currently working on, allowing for quick access and manipulation during arithmetic and logic operations.
Memory Cards and Modules
Memory cards and modules, such as SD cards, microSD cards, and DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Modules), are standardized storage solutions used in various electronic devices, including cameras, smartphones, tablets, and computers.
MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random-Access Memory) Modules
MRAM modules are a new type of non-volatile memory that uses magnetic elements to store data. They offer fast access times, low power consumption, and robust data retention, making them promising candidates for future memory technologies.
Memory modules are the backbone of data storage and retrieval in electronic devices. From providing fast temporary storage in RAM to long-term data retention in non-volatile memory, these modules play a crucial role in enabling seamless and efficient data handling across various industries and applications. As technology continues to advance, memory modules will continue to evolve, offering higher capacities, faster access times, and more innovative solutions to meet the growing demands of the digital age.

Audio Modules
Audio modules are specialized components in electronic devices that enhance sound quality, provide audio processing functionalities, and enable seamless audio communication. From delivering immersive audio experiences in multimedia devices to providing crystal-clear audio in communication systems, audio modules play a vital role in enhancing user engagement and overall audio performance. In this section, we will explore the various types of audio modules and their significance in modern electronic applications.
Audio Amplifier Modules
Audio amplifier modules are responsible for increasing the power of audio signals to drive speakers or headphones. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the audio output is loud and clear, providing a rich and immersive listening experience in devices such as audio systems, smartphones, and home theater setups.
Audio Codec Modules
Audio codec modules handle the conversion of analog audio signals to digital and vice versa. They are used in audio recording, playback, and communication applications, ensuring accurate representation and transmission of audio data.
Speaker Modules
Speaker modules consist of speakers housed in a compact and optimized form factor. They are commonly used in various electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and portable audio players, to produce sound with high fidelity and clarity.
Microphone Modules
Microphone modules capture audio signals and convert them into electrical signals. They are essential components in communication devices, voice recognition systems, and audio recording devices, allowing clear and precise audio input.
Audio Processing Modules
Audio processing modules are equipped with signal processing capabilities to modify audio signals. They are used in audio effects processors, equalizers, noise reduction systems, and audio enhancement features found in many consumer electronics.
Bluetooth Audio Modules
Bluetooth audio modules enable wireless audio streaming between devices, providing the freedom to listen to music, make calls, and watch videos without the constraints of wires. They are commonly used in wireless headphones, speakers, and car audio systems.
Sound Cards
Sound cards are audio modules integrated into computers to process and manage audio signals. They are essential for high-quality audio output and input in gaming, multimedia production, and general computer audio applications.
Audio DSP (Digital Signal Processing) Modules
Audio DSP modules are designed to handle complex audio processing tasks, such as real-time audio effects and audio synthesis. They find applications in audio recording studios, music production, and digital musical instruments.
Audio Mixers
Audio mixers combine multiple audio inputs and allow users to adjust the volume levels and add various audio effects. They are commonly used in professional audio setups, live performances, and multimedia production to achieve balanced audio output.
Audio Communication Modules
Audio communication modules enable voice communication in various devices, including smartphones, intercom systems, and walkie-talkies. They provide clear audio transmission and reception, facilitating efficient two-way communication.
Audio modules play a pivotal role in elevating audio experiences and enabling seamless audio communication in electronic devices. From high-fidelity sound reproduction to advanced audio processing capabilities, these modules contribute to the enjoyment and functionality of audio-related applications across diverse industries. As technology advances, audio modules will continue to evolve, offering even more innovative solutions for enhancing audio quality and capabilities in the digital age.

Motor Control Modules
Motor control modules are specialized electronic components that regulate the operation of motors and actuators. These intelligent units enable precise control over motor speed, direction, and torque, making them essential in various applications, from industrial automation to robotics and automotive systems. In this section, we will explore the significance and functionalities of motor control modules.
Types of Motor Control Modules
This subsection will discuss the different types of motor control modules available in the market, including:
- DC Motor Control Modules: These modules regulate the speed and direction of direct current (DC) motors using pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques.
- Stepper Motor Control Modules: These modules provide accurate control over the rotation of stepper motors, making them ideal for precise positioning applications.
- Servo Motor Control Modules: These modules enable precise control over the position, speed, and torque of servo motors, commonly used in robotic and automation systems.
- BLDC Motor Control Modules: Designed for brushless DC motors, these modules offer efficient and reliable motor control, commonly used in electric vehicles and drones.
Features and Functionality
In this section, we will delve into the key features and functionalities of motor control modules, including:
- PWM Generation: The ability to generate pulse-width modulation signals to control motor speed.
- Direction Control: The capability to change the direction of motor rotation for bidirectional motion.
- Speed Control: The ability to adjust the motor speed based on input signals or feedback from encoders.
- Acceleration and Deceleration: Built-in profiles for smooth acceleration and deceleration of motor movement.
- Current Limiting and Overload Protection: Ensuring safe operation by limiting motor current and protecting against overload conditions.
Applications of Motor Control Modules
This subsection will highlight the wide range of applications where motor control modules are instrumental, such as:
- Industrial Automation: Motor control modules are crucial in controlling conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other automated systems.
- Robotics: In robotics, these modules enable precise control over the movement of robotic limbs and joints.
- Automotive Systems: Motor control modules are used in electric power steering, electric window control, and other automotive applications.
- Consumer Electronics: They find applications in camera stabilization, drones, and home appliances.
Motor Feedback and Closed-Loop Control
Here, we will discuss the importance of motor feedback and how closed-loop control systems use feedback from encoders and sensors to ensure precise motor positioning and stable operation.
Communication Interfaces
This section will cover the communication interfaces provided by motor control modules, such as UART, SPI, and I2C, which allow seamless integration with microcontrollers and other electronic devices.
Advanced Motor Control Techniques
This subsection will explore advanced motor control techniques, including field-oriented control (FOC) for BLDC motors, sensorless control, and vector control, which enhance motor efficiency and performance.
Motor Control Development Kits
Finally, we will discuss motor control development kits available in the market, which provide ready-to-use solutions for designing motor control systems, accelerating the development process for engineers and hobbyists.
Application-Specific Modules
Application-specific modules are specialized electronic components designed to cater to the unique requirements of specific applications or industries. These intelligent units offer dedicated functionalities, pre-built circuits, and optimized interfaces, streamlining the development process and enhancing the performance of targeted systems. From GPS tracking and biometric recognition to RFID communication and camera integration, application-specific modules play a pivotal role in solving complex challenges and delivering efficient solutions.
GPS Modules: Navigating with Precision
GPS modules are designed to receive signals from global positioning system (GPS) satellites and provide accurate location and timing information. They are widely used in navigation devices, vehicle tracking systems, asset tracking, and location-based services, enabling precise positioning and reliable navigation capabilities.
Camera Modules: Capturing Visual Data
Camera modules are integrated imaging solutions that capture visual data in electronic devices. They are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, surveillance cameras, and drones, providing high-quality image and video capture for various applications, from photography to video conferencing.
Biometric Modules: Identifying with Uniqueness
Biometric modules are specialized components that use biometric data, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial features, for identification and authentication purposes. They find applications in smartphones, access control systems, and secure authentication processes, ensuring enhanced security and user convenience.
RFID Modules: Enabling Wireless Communication
RFID modules facilitate contactless data exchange between electronic devices using radio frequency (RF) signals. They are used in access control, inventory management, payment systems, and tracking applications, offering efficient and convenient wireless communication capabilities.
IoT (Internet of Things) Communication Modules: Connecting the World
IoT communication modules provide the necessary connectivity for IoT devices to exchange data over the internet. They support various IoT communication protocols, such as MQTT, CoAP, and LoRaWAN, enabling seamless integration of IoT devices into larger networks.
Sensor Fusion Modules: Combining Sensor Data
Sensor fusion modules integrate data from multiple sensors, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, to provide comprehensive and accurate information about a device’s orientation and movement. They are commonly used in robotics, virtual reality systems, and motion-capture applications.
Voice Recognition Modules: Interacting with Speech
Voice recognition modules enable devices to process and interpret human speech, providing voice-controlled functionalities. They are used in virtual assistants, voice-activated smart home devices, and speech-to-text applications, enhancing user interaction and accessibility.
Power Control Modules: Managing Energy Efficiently
Power control modules optimize energy consumption in electronic devices, helping to prolong battery life and enhance power efficiency. They may include power management ICs, voltage regulators, and battery charging circuits, ensuring optimal power utilization in various applications.
Industrial Automation Modules: Streamlining Industrial Processes
Industrial automation modules are designed to meet the specific demands of industrial applications, such as PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) modules, motor control modules, and communication modules tailored for industrial networking protocols like Modbus and Profibus.
RF (Radio Frequency) Modules
RF (Radio Frequency) modules are specialized electronic components that facilitate wireless communication over radio frequencies. These intelligent units play a crucial role in enabling data transmission and reception without the need for physical cables. RF modules are used in a wide range of applications, from wireless communication in consumer electronics to industrial telemetry, remote control systems, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices. In this section, we will explore the various aspects of RF modules and their significance in modern wireless communication.
What are RF Modules?
An introduction to RF modules, explaining their basic function and role in wireless communication systems. RF modules consist of transmitters and receivers that use radio waves to send and receive data over the airwaves.
Types of RF Modules
An overview of the different types of RF modules available, including RF transmitters, RF receivers, and transceiver modules that combine both transmitter and receiver functionalities.
RF Communication Protocols
Explanation of various RF communication protocols, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, LoRa, and RFID, which are commonly used in RF modules to enable seamless wireless data exchange between devices.
RF Frequency Bands
An overview of the different RF frequency bands used in RF modules, including popular bands such as 2.4 GHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz, and their respective applications and advantages.
Applications of RF Modules
Exploring the wide range of applications where RF modules are utilized, such as wireless communication in smartphones, smart home devices, remote controls, keyless entry systems, telemetry in industrial applications, and wireless sensor networks in IoT devices.
RF Range and Transmission Power
Discussions on RF module range and transmission power, including factors that affect the range of RF communication and techniques to improve the communication distance.
Security in RF Communication
An overview of the security measures used in RF communication to protect data from unauthorized access and interception, including encryption and authentication protocols.
Antennas for RF Modules
The role of antennas in RF modules and their impact on communication range and performance. Different types of antennas, such as whip antennas, patch antennas, and PCB (Printed Circuit Board) antennas, and their respective applications.
Integration with Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems
Exploring how RF modules are integrated into microcontroller-based systems and embedded devices and the communication interfaces used to interface RF modules with microcontrollers.
Challenges and Future of RF Modules
Discussion of the challenges faced in RF communication, such as interference, multipath fading, and spectrum congestion, as well as advancements and future trends in RF module technology, including improved efficiency, low power consumption, and higher data rates.

Power Supply Modules
Power supply modules are essential components in electronic systems that provide the necessary electrical energy to various components and circuits. These intelligent units regulate and convert the input voltage to deliver a stable and reliable power output, ensuring the smooth operation of electronic devices. From small voltage regulators to high-power switching power supplies, power supply modules play a critical role in powering everything from simple gadgets to complex industrial systems. In this section, we will explore the different types of power supply modules and their significance in modern electronics.
Linear Power Supply Modules: Simple and Reliable
Linear power supply modules use linear regulators to reduce the voltage from the input source to the desired output level. They provide a clean and stable DC output and are suitable for applications where low noise and precise regulation are essential. Linear power supplies are commonly used in audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and applications where simplicity and reliability are key.
Switching Power Supply Modules: Efficiency and Compactness
Switching power supply modules use high-frequency switching techniques to regulate and convert the input voltage efficiently. They are capable of handling higher power levels and are generally more energy-efficient than linear power supplies. Switching power supplies are widely used in computers, consumer electronics, LED lighting, and other applications where space and energy efficiency are important.
AC-DC Power Supply Modules: Converting Alternating to Direct Current
AC-DC power supply modules convert alternating current (AC) from the mains to the required direct current (DC) voltage. They are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including laptops, smartphones, routers, and industrial equipment, to provide the necessary DC power for their operation.
DC-DC Converter Modules: Matching Different Voltage Levels
DC-DC converter modules convert one DC voltage level to another, enabling compatibility between components with different voltage requirements. They are commonly used in battery-powered devices, where the input voltage may vary due to battery depletion, ensuring a stable output voltage for consistent performance.
Modular Power Supply Units: Versatility and Scalability
Modular power supply units consist of multiple interchangeable power supply modules that can be combined to meet specific power requirements. They provide flexibility and scalability in power delivery, making them suitable for data centers, telecommunications, and industrial applications with varying power demands.
DIN Rail Power Supply Modules: Designed for Industrial Use
DIN rail power supply modules are specifically designed for industrial applications, where reliability, ruggedness, and safety are crucial. These modules can be mounted on standard DIN rails, making them easy to install in industrial control panels, automation systems, and factory environments.
Open Frame Power Supply Modules: Space-Saving Solutions
Open-frame power supply modules are compact units without external casing, suitable for space-constrained applications. They are commonly used in small electronics, embedded systems, and applications where form factor and space-saving are critical.
Rack-Mount Power Supply Modules: Centralized Power Distribution
Rack-mount power supply modules are designed to be installed in standard server racks, providing centralized power distribution for multiple devices in data centers, telecommunications, and networking applications.
Redundant Power Supply Modules: Ensuring Continuous Operation
Redundant power supply modules are used in critical systems to ensure continuous operation in case of a power supply failure. These modules provide backup power, minimizing downtime and enhancing system reliability.
High-Voltage Power Supply Modules: Specialized for High-Voltage Applications
High-voltage power supply modules are designed to handle and regulate high voltage levels required in specific applications, such as scientific experiments, medical equipment, and specialized industrial processes.
Wireless Charging Modules
Wireless charging modules are innovative electronic components that enable the transfer of electrical energy without the need for physical connectors or cables. These intelligent units have revolutionized the way we power and charge our electronic devices, providing a more convenient and cable-free charging experience. From smartphones and wearables to electric vehicles and IoT devices, wireless charging modules have become increasingly popular and are reshaping the future of power delivery. In this section, we will explore the different aspects of wireless charging modules and their significance in modern electronics.
How Wireless Charging Works: The Basics
This section will provide an overview of the basic principles behind wireless charging. It will explain the concept of electromagnetic induction and resonant coupling, which are the two primary methods used for wireless power transfer. The section will also describe the components involved in wireless charging, such as the transmitter (charging pad or dock) and the receiver (charging coil in the device).
Inductive Wireless Charging Modules: Efficient and Widespread
Inductive wireless charging modules use electromagnetic induction to transfer power between the transmitter and receiver coils. This section will explain the inductive charging process, its efficiency, and its widespread adoption in various consumer electronic devices like smartphones, smartwatches, and wireless earbuds.
Resonant Wireless Charging Modules: Extending the Range
Resonant wireless charging modules use resonant coupling to achieve longer-distance power transfer and alignment flexibility. This section will explore the resonant charging technology and its benefits, including the ability to charge multiple devices simultaneously and the potential for future advancements in wireless charging technology.
Qi Standard: A Universal Approach
The Qi standard, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC), has become the de facto standard for wireless charging. This section will discuss the Qi standard’s role in promoting interoperability among wireless charging devices and how it has facilitated the widespread adoption of wireless charging technology.
Advantages and Challenges of Wireless Charging
This section will provide an overview of the advantages of wireless charging, such as convenience, cable clutter reduction, and enhanced device protection (through sealed charging ports). It will also address the challenges, including charging speed, alignment issues, and potential energy losses during wireless power transfer.
Wireless Charging Applications
In this section, we will explore the various applications of wireless charging modules across different industries. This will include consumer electronics, automotive (electric vehicles), medical devices, IoT devices, and industrial automation, showcasing how wireless charging is transforming various sectors.
Future of Wireless Charging
This section will discuss the potential future developments and innovations in wireless charging technology. It will touch on topics such as longer-range charging, integration with smart surfaces, and advancements in fast-charging capabilities.
Considerations for Wireless Charging Adoption
For individuals or businesses considering the adoption of wireless charging, this section will provide essential considerations, such as compatibility, device positioning, charging pad specifications, and safety aspects.
Eco-Friendly Aspects of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging can also have positive environmental impacts. This section will discuss how wireless charging can reduce the need for disposable charging cables, promote energy efficiency, and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable charging ecosystem.
IoT (Internet of Things) Modules
IoT modules are specialized components that form the backbone of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and exchange data over the Internet. These intelligent units provide the necessary hardware and software functionalities to transform ordinary objects into smart and interconnected devices. From sensor data collection to cloud connectivity, IoT modules play a crucial role in building the foundation for a connected and data-driven world. In this section, we will explore the different types of IoT modules and their significance in the rapidly growing IoT landscape.
IoT Communication Modules: Connecting Devices Wirelessly
IoT communication modules provide the essential wireless connectivity options for IoT devices to communicate over the internet. They support various communication protocols, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and cellular networks, allowing IoT devices to transmit data to the cloud and interact with other devices seamlessly.
IoT Sensor Modules: Capturing Real-World Data
IoT sensor modules include a variety of sensors that capture data from the surrounding environment. They can include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, motion sensors, light sensors, gas sensors, and more. These modules play a crucial role in collecting valuable data for IoT applications, such as environmental monitoring, industrial automation, and smart home systems.
IoT Edge Computing Modules: Processing Data Locally
IoT edge computing modules enable data processing and analysis to be performed at the edge of the network, closer to the IoT devices. By processing data locally, these modules reduce latency, bandwidth usage, and dependency on cloud services, making IoT systems more responsive and efficient.
IoT Gateway Modules: Bridging the Gap
IoT gateway modules act as intermediaries between IoT devices and the cloud or central server. They collect data from local IoT devices, perform protocol translation, and securely transmit the data to the cloud for storage and further processing. IoT gateways are essential for managing and coordinating large-scale IoT deployments.
IoT Cloud Connectivity Modules: Linking Devices to the Cloud
IoT cloud connectivity modules provide the necessary protocols and security mechanisms to establish a connection between IoT devices and cloud services. They enable devices to transmit data to the cloud, receive updates, and interact with cloud-based applications and services.
IoT Security Modules: Safeguarding IoT Ecosystems
IoT security modules offer robust security features to protect IoT devices and networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. They may include hardware security modules (HSMs), encryption algorithms, secure boot mechanisms, and authentication protocols to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of IoT data.
IoT Power Management Modules: Optimizing Energy Consumption
IoT power management modules are designed to maximize energy efficiency in IoT devices, especially in battery-powered applications. They may include low-power microcontrollers, power-saving modes, and energy-harvesting techniques to prolong battery life and reduce overall energy consumption.
IoT Firmware and Software Modules: Enabling Device Intelligence
IoT firmware and software modules provide the necessary programming and intelligence to IoT devices. They control device operations, data processing, and interaction with other devices and services. IoT firmware and software modules are critical for creating smart and autonomous IoT applications.
IoT Development Kits and Modules: Simplifying IoT Prototyping
IoT development kits and modules offer pre-built hardware and software solutions, enabling developers to prototype and test IoT applications quickly. These kits often include microcontrollers, sensors, communication interfaces, and development tools, streamlining the IoT development process.
IoT Analytics Modules: Extracting Insights from Data
IoT analytics modules process and analyze the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices. They utilize techniques such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to extract valuable insights from the data, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and data-driven decision-making.
IoT modules are at the heart of the IoT revolution, enabling the seamless integration of smart devices and creating a more interconnected and data-rich world. With their diverse functionalities and capabilities, IoT modules empower industries, businesses, and individuals to harness the potential of IoT technology and drive innovation in various sectors. As IoT continues to evolve, these modules will play a critical role in shaping the future of connected devices and IoT-driven applications.

Embedded System Modules
Embedded system modules are specialized components designed to operate as integral parts of embedded systems. These intelligent units are optimized to provide specific functionalities and seamless integration into a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial automation and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. By combining processing power, communication capabilities, and various interfaces, embedded system modules enable the development of intelligent, connected, and efficient electronic systems. In this section, we will explore the diverse types of embedded system modules and their significance in modern electronic applications.
Microcontroller Modules: The Brains of Embedded Systems
Microcontroller modules are the heart of many embedded systems, integrating a CPU, memory, I/O peripherals, and communication interfaces into a single chip. They are used in countless applications, such as home appliances, automotive control units, smart home devices, and wearables, providing the processing power and control necessary for these systems to function.
System-on-Chip (SoC) Modules: Combining Power and Integration
SoC modules take microcontrollers to the next level by integrating additional components, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), wireless communication modules, and cryptographic accelerators, onto a single chip. SoCs are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and other advanced electronic devices that require high-performance computing and connectivity.
Communication Modules: Enabling Seamless Connectivity
Communication modules for embedded systems provide various wireless and wired communication options, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa, cellular, Ethernet, and more. These modules facilitate data exchange and networking capabilities, allowing embedded systems to connect and interact with other devices, servers, and the Internet.
Sensor Interface Modules: Connecting to the Physical World
Sensor interface modules enable embedded systems to interact with a wide range of sensors, including temperature sensors, motion sensors, environmental sensors, and more. They provide the necessary analog-to-digital conversion and signal conditioning to process data from sensors, making them essential for applications that require real-world data input.
Power Management Modules: Efficiently Managing Energy
Power management modules optimize the energy consumption of embedded systems, extending battery life and enhancing power efficiency. They may include voltage regulators, battery charging circuits, and power monitoring features, ensuring optimal power utilization in battery-powered devices.
Memory Modules: Storing and Retrieving Data
Memory modules in embedded systems provide temporary and permanent data storage solutions. They include RAM for fast data access during program execution, non-volatile memory for critical data retention, and external storage options like flash memory or SD cards for data storage and transfer.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Modules: Enhancing User Interaction
HMI modules enable interaction between users and embedded systems, providing displays, touchscreens, buttons, and other input/output interfaces. They enhance the user experience by providing intuitive ways to control and monitor the embedded system’s behavior.
Real-Time Clock (RTC) Modules: Keeping Time Accurately
RTC modules provide accurate timekeeping capabilities for embedded systems, even when the main power source is disconnected. They are essential for time-sensitive applications, such as logging data with timestamps and managing scheduled tasks.
Security Modules: Safeguarding Embedded Systems
Security modules enhance the security of embedded systems by implementing cryptographic algorithms, secure boot mechanisms, and secure communication protocols. They protect against unauthorized access, tampering, and data breaches, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Motor Control Modules: Managing Mechanical Movements
Motor control modules enable precise control over motors and actuators in embedded systems, ensuring smooth and efficient mechanical movements. They are used in robotics, automation systems, automotive applications, and more, allowing for accurate positioning and motion control.
RFID/NFC (Near Field Communication) Modules
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and NFC (Near Field Communication) modules are specialized components that enable contactless data exchange between electronic devices using radio frequency signals. These intelligent units have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, providing seamless and convenient wireless communication in various applications. From access control and payment systems to inventory management and smart devices, RFID/NFC modules play a pivotal role in simplifying transactions, enhancing security, and enabling innovative user experiences. In this section, we will explore the functionalities and applications of RFID/NFC modules with specific headings.
RFID Technology: Tracking and Identifying Objects
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify and track objects equipped with RFID tags. RFID modules consist of a reader and an antenna that can communicate with RFID tags at different frequencies. They find applications in asset tracking, supply chain management, toll collection, and electronic payment systems.
NFC Technology: Simplifying Wireless Communication
NFC technology enables short-range wireless communication between devices when they are brought into proximity. NFC modules operate at 13.56 MHz and can operate in both active and passive modes. They are commonly used for contactless payment, ticketing, smart access cards, and pairing Bluetooth devices.
RFID/NFC Tag Modules: Enabling Data Storage
RFID/NFC tag modules are passive components that contain a microchip and an antenna for data storage and wireless communication. They are used to attach information to physical objects, enabling easy identification and data retrieval when scanned by an RFID/NFC reader.
RFID/NFC Reader Modules: Initiating Communication
RFID/NFC reader modules consist of an antenna and a reader circuit that can communicate with RFID/NFC tags. When an RFID/NFC tag is brought near the reader, the module initiates communication, reads the tag’s data, and performs the necessary actions based on the application’s requirements.
Contactless Payment: Enhancing Transactions
RFID/NFC modules have transformed the payment industry, enabling contactless payment solutions. With a simple tap of a card or a smartphone, users can make secure and swift transactions at point-of-sale terminals, reducing the need for physical contact and enhancing user convenience.
Smart Access Control: Simplifying Entry Systems
RFID/NFC modules are widely used in access control systems to manage the entry and exit of authorized personnel. Employees can use RFID/NFC cards or smartphones to access secure areas, offices, and buildings, enhancing security and streamlining access management.
Inventory Management: Improving Efficiency
In inventory management, RFID/NFC modules help track and monitor items throughout the supply chain. By attaching RFID/NFC tags to products, manufacturers, retailers, and logistics companies can efficiently manage stock levels, monitor shipments, and improve overall inventory accuracy.
Smart Devices and IoT Integration: Enhancing Connectivity
RFID/NFC modules play a vital role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling connectivity and interaction between smart devices. They are used in smart home systems, wearables, and industrial IoT applications, allowing devices to communicate and share information seamlessly.
Healthcare Applications: Enhancing Patient Care
In the healthcare sector, RFID/NFC modules are used for patient identification, medication management, and asset tracking. By tagging patient wristbands and medical equipment, healthcare providers can improve patient safety and streamline inventory management.
Innovation and Future Applications
As RFID/NFC technology continues to advance, new applications and use cases will emerge. From interactive marketing and gaming to secure authentication and contactless interactions, the potential for RFID/NFC modules to revolutionize various industries and enhance user experiences is boundless.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of electronics is enriched by an array of intelligent modules, each catering to specific functionalities and applications. From powering motors and managing data to enabling seamless communication and enhancing audio and visual experiences, these specialized units play a pivotal role in shaping the functionality and performance of modern electronic devices. Whether it’s the precision of motor control modules, the convenience of RFID/NFC modules, or the immersive audio from audio modules, these intelligent components have revolutionized the way we interact with technology. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in these modules, unlocking even more innovative solutions for diverse industries and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of electronics.
FAQs about Types of Modules
1. What are electronic modules?
Electronic modules are self-contained units that encapsulate specific functionalities, components, or circuits into a single package. They are designed to be easily integrated into larger electronic systems, simplifying the overall design process and enhancing the performance and reliability of the end product.
2. What are some common types of modules in electronics?
Some common types of modules in electronics include motor control modules, audio modules, communication modules (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), power modules, and display modules.
3. What is the significance of motor control modules?
Motor control modules regulate the operation of motors and actuators, enabling precise control over motor speed, direction, and torque. They are essential in robotics, automation, electric vehicles, and various industrial applications that require efficient and accurate motion control.
4. How do RFID/NFC modules work?
RFID/NFC modules use radio frequency signals to enable contactless data exchange between electronic devices. RFID technology identifies and tracks objects equipped with RFID tags, while NFC technology facilitates short-range wireless communication when devices are brought into proximity.
5. What applications benefit from RFID/NFC modules?
RFID/NFC modules have diverse applications, including contactless payment, access control systems, inventory management, smart devices, and healthcare. They enhance security, streamline transactions, and simplify interactions in various industries and IoT ecosystems.